Engineers and technicians doing design, development, and testing have a wide range of instrumentation available for use on the test bench. So it might be useful to consider which instruments are considered the “basics” for the general case. Here are a few nominations along with the device properties that are generally considered “must-haves.”

A related test instrument is an incandescent bulb screwed into a socket that can be plugged into a standard receptacle. Sometimes this simple bulb works better than a multimeter in situations where it is difficult for multimeter probes to make contact. One or more of these testers can be left in place and viewed from a distance while troubleshooting branch circuits. Also, you can plug one of them, equipped with an appliance bulb, into an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) to check the condition of the internal battery. The bulb should remain at full brightness for about an hour after the unit is unplugged.

In amps mode the multimeter is limited to low current levels, at most 10 A. It is protected by an internal glass fuse, but overloading can damage the meter and circuit under investigation before the fuse blows. The other disadvantage in using a multimeter to measure current is that the instrument must be placed in series with the source or load. This usually involves cutting a wire or lead and later resoldering it. These difficulties are avoided by using a clamp-on ammeter.

On a smaller scale, clamp-on current probes are available for use with oscilloscopes. They are expensive options but worthwhile for displaying current waveforms. Voltage waveforms, using a 10:1 or other appropriate probe, can be displayed in a separate channel and then, using the Math dual Waveform mode, the two values can be multiplied to obtain a power reading.
When the amount of current is too low to display, the wire can be coiled so that it passes through the jaws two or more times, multiplying the intensity of the magnetic flux. The higher reading then must be divided to obtain the correct result.
In measuring current or voltage, the user must be aware of the instrument impedance. Impedance is the vectorized sum of resistance and capacitive or inductive reactance. When taking a current measurement, a low-impedance instrument has little effect on the circuit under investigation. When taking a voltage measurement, it has a large effect. A high-impedance instrument taking a voltage measurement in parallel with the source or load is essentially invisible.

Also called a solenoid voltmeter, the Wiggy has medium impedance. Connected to a dc source, it makes a highly audible click. The buzzing it makes when connected to an ac source is useful in low-light. Because of the moderate impedance, the solenoid voltmeter is useful for checking a GFCI to see if it will trip when the Wiggy’s leads are touched to neutral and equipment ground on the load side of the device.
The modern digital storage oscilloscope is a versatile instrument with endless features and capabilities. In either bench or hand-held versions, this 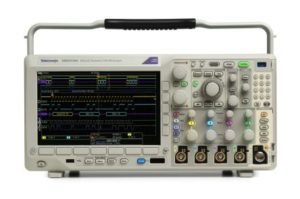
Shortly after triggered sweep was introduced following its development for radar during World War Two, the oscilloscope became widely used in conjunction with the AFG for servicing TV’s. An RF waveform was injected downstream from the tuner and accessed at successive stages to find the source of any distortion or signal loss. This procedure worked at circuit and component levels as well. The oscilloscope quickly became the most-used instrument in every electronics lab, workshop and classroom worldwide.
Its close relative, the spectrum analyzer, operates exclusively in the frequency domain. In that role its vast display and signal processing characteristics permit the user to peer deeper into the wave mechanics that animate our universe.
Besides the test and measurement instruments mentioned above, many others come in handy.
• The curve tracer is a highly intelligent, interactive instrument. It applies a swept signal to a semiconductor device and displays the response. As the name implies, it incorporates a flat screen, originally a cathode ray tube. A swept voltage whose amplitude automatically varies in time is typically applied to transistors in common-base and common-emitter configurations, and a trace showing the collector current displays. Looking at a diode, the curve tracer shows forward voltage, reverse leakage current, reverse breakdown voltage and other parameters.
• The distortion meter, also known as distortion factor meter, measures the amount of distortion contributed by harmonics. It measures a signal before and after the harmonics are subtracted. The instrument consists of switchable inputs. One circuit reads the total signal. When the distortion level is low, it is close to the pure fundamental, which is set at 100% (0 dB). The other circuit removes the fundamental by means of a notch filter so the amount of distortion is displayed.
• The network analyzer measures parameters of electrical networks, particularly of amplifiers and filters having dual ports. It is generally operated at high frequencies, up to 1.05 tHz. There are two types, the scalar network analyzer, which measures amplitude only, and the vector network analyzer, which measures both amplitude and phase. While a scalar network analyzer resembles a spectrum analyzer, the combination vector instrument, used primarily in RF design applications, is more common today.
Finally, we’ll end with mentions of instruments that are less common on the average test bench but nevertheless have a place in more specialized situations.
• The Q-meter measures the Q factor of RF circuits. (It has largely been replaced by vector network analyzers.)
• A signal analyzer measures amplitude and modulation of an RF signal.
• A sweep generator creates constant-amplitude, variable-frequency sine waves to test frequency response.
• A vectorscope displays the phase of TV color signals.
• A video signal generator creates a video signal for testing purposes.
• A VU meter measures audio signals in volume units.



Who can pay these days MDO3104 which still costs on EBay us$9000-12500?
C’mon Joe quit complaining and turn in your cans and bottles like everyone else and soon you can afford to play with toys like the big boys.