Where there is matter, there is the potential for free electrons, and unless the temperature is absolute zero, these electrons exhibit random motion. Thus the basis for noise in electronic circuits. In metals such as copper, the number of these free electrons is large and their motion appears to be independent and truly random. Electronics […]
oscilloscope measurements
Understanding basic oscilloscope uses
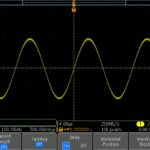
The dominant oscilloscope type today is digital. A relatively small number of analog oscilloscopes are still made for educational purposes and low-end DIY kits. The digital revolution in oscilloscope design, initiated by Walter LeCroy over 50 years ago, made possible vast new capabilities and features. Still, it is worthwhile for perspective to look back at […]
Budget-priced transistor testing
The field-effect transistor (FET) in one form or another has largely superseded the earlier bipolar junction transistor (BJT). Both can do amplification, oscillation, and switching, but the methods in getting there are quite different as are the input and output impedances. First, by way of background, we’ll look back at the BJT. It contains three […]
Quantifying signal compression
The object of signal compression is to facilitate transmission, reception, processing, and the use of great amounts of data while conserving valuable storage space and transmission resources. Data compression is obviously a good approach provided that it doesn’t incur an unacceptable amount of information loss. It was once widely assumed that detail or information, once […]
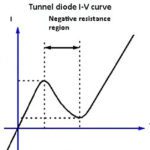
Negative resistance: meaning and measurement
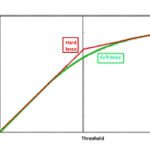
It is a fact, verified in theory and by experiment, that no material can conduct electric current with greater efficiency than an ideal conductor having zero resistance. How, then, can the term “negative resistance” have meaning in the real world? First, it is possible to get negative resistance readings on a DVM. If this happens, they […]
Measuring active and passive filters
The usual rationale for a filter in electronic circuitry is to reject unwanted portions of a spectrum or at least reduce their amplitudes to acceptable levels without attenuating the desired frequency or range of frequencies. In some situations, active filters are needed to perform this function, and often they are less expensive than alternate solutions […]
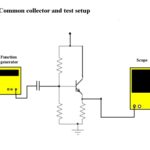
Measuring emitter followers and other transistor configurations
There are three bipolar junction transistor amplifier topologies: common emitter, common base and common collector. (For field-effect transistors, the analogous circuit configurations are common source, common gate and common drain. In the old world of vacuum tubes, they were common cathode, common grid and common plate.) This particular classification derives from the external circuit configuration. […]
Dealing with and displaying power-line harmonics
Harmonics are waveforms that may accompany a periodic fundamental (also known as the first harmonic) in a divergent infinite series. When they arise, their frequencies are integer multiples of the fundamental. If this fundamental is 60 Hz, the second harmonic is 120 Hz, the third harmonic is 180 Hz, the fourth harmonic is 240 Hz […]
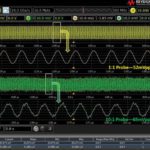
How to reduce oscilloscope noise during measurements
Several tricks can help reveal small signals that are obscured by measurement system noise. KENNY JOHNSON KEYSIGHT TECHNOLOGIES, INC. THERE is a need to observe small signal details in many modern applications. Transducers, biomedical sensors, high energy physics, power integrity, and high-speed digital designs are examples of situations where details can be obscured by measurement […]
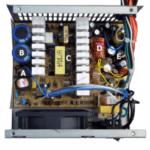
Switching power supply: How to test and use in applications
The two major types of power supplies, linear and switch mode (SMPS), operate according to entirely different principles and have distinguishing characteristics. Design work and maintenance on each one requires totally different mindsets. The SMPS is now widely used because of its greater efficiency, lower cost and better weight and thermal qualities. There are some […]