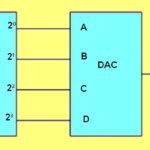
A digital-to-analog converter (DAC) is more prone than an analog/digital converter to signal degradation. DACs are complex devices requiring precisely matched components. For this reason, with notable exceptions, DACs are implemented as mixed-signal ICs based on MOSFET technology. Discrete component DACs are found in radar systems and high-speed test equipment including digital sampling oscilloscopes. Digital […]
texasinstruments
The up side of under sampling
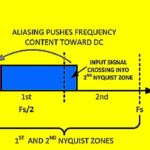
A digital signal can be derived from the original time-varying, continuous analog signal by creating a sampled sequence of quantized values. It is intuitively evident that the fidelity and resolution of this quantized signal is based upon the number of samples taken per unit of time. Harry Nyquist published an early version, later further formalized […]
Measuring CMOS power use
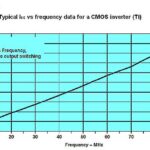
Virtually all digital, analog and mixed-signal ICs are now done in CMOS due to the technology’s extremely low power consumption, small size and immunity to noise. Low power consumption arises from the use of a two-transistor configuration resulting in zero power consumption except during brief transitions. Interestingly, the bulk of CMOS power dissipation arises because […]
Measuring picoseconds without breaking the bank
Modern analog/digital converters can help implement equivalent time sampling to provide picosecond timing resolution. Dave Guidry, Texas Instruments Inc. A picosecond is an astonishingly short period of time. Imagine a stopwatch with a trillion divisions between each tick of the second hand. While it sounds fantastical, this resolution of time measurement is indeed necessary for […]
When you can use Spice and its variants, when you can’t
It has been a long time since it was practical to breadboard even moderately complex IC designs to evaluate them prior to manufacture. This is particularly true because of subtle parasitic and characteristic impedance effects that rear their ugly head in the frequency ranges of many modern circuit designs. That is the rationale for Spice […]
Tools for optimizing circuit bias
If a semiconductor or vacuum tube is to accurately reproduce or amplify signals on its input, it must have on its input a non-time-varying dc voltage, i.e. dc bias, the purpose of which is to keep the device in its linear operating range. Otherwise, the input signal to be reproduced may drive the device beyond […]