By Lisa Clark Before we differentiate a spectrum analyzer and a network analyzer, it is important to understand what these two instruments are, and what function they perform. Thus, we give a basic overview of the two devices and their basic mechanism: Spectrum Analyzer The spectrum analyzer is an electronic device that is used for […]
FAQ
Joseph Henry and mutual inductance
Joseph Henry (1797-1878) discovered the phenomenon of mutual inductance independently and more or less simultaneously with Michael Faraday. Because Faraday published his results a little earlier, he received credit for the discovery. But due to the large volume and quality of his published research, Henry gained stature early in life. He was six years younger […]
Basics of quartz crystal oscillators
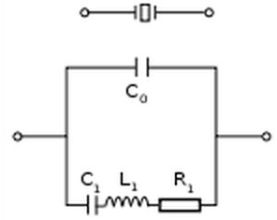
By David Herres Some materials acquire an electrical charge when they are compressed or otherwise dimensionally stressed. They are said to exhibit the piezoelectric effect. If the property is to be manifest on any but an atomic level, the material must be a crystal, with the atoms organized in a lattice. The piezoelectric effect was […]
Basics of oscillators
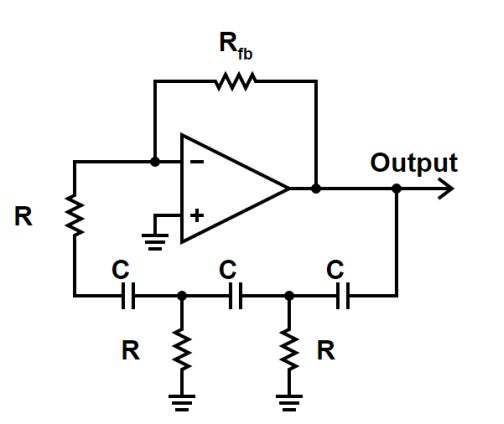
A previous article discussed resonant circuits. Now we’ll go on to look at that fundamental workhorse of the modern electronic world, the oscillator. Without it, radio and TV transmission and reception as we know them would not be possible. There are countless other applications, from the microwave oven with its high-frequency force field, to the […]
ICs and timers
Moore’s law, actually more an observation than an edict, states that the number of transistors that can sit on a single semiconductor chip may be expected to double every two years. (Another version sets the time frame as 18 months.) The assertion is flawed because it suggests that before long the device population on a single chip […]
Basics of CMOS
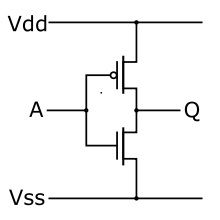
By David Herres Complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) is a highly successful strategy for combining complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSFETs to create logic functions. A CMOS transistor pair is typically a building block for integrated circuits. Among its many applications are image sensors in digital cameras, data converters and transceivers. In a […]
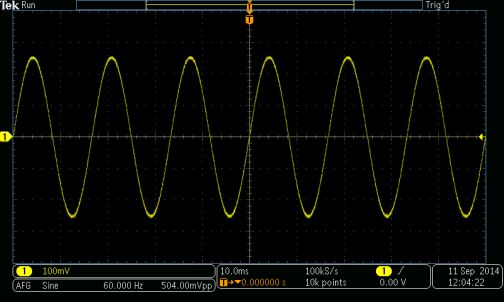
Sine wave basics and applications in oscilloscopes
By David Herres Oscilloscopes typically display the amplitude of a signal on the Y axis as a function of time on the X axis. The resulting display can take the form of a straight horizontal line if it is a dc voltage, an irregular non-recurring and intermittent pattern for complex signals such as the human voice, […]
How much bandwidth?
The cost of an oscilloscope depends primarily on its bandwidth and, to a lesser degree, on added features such as an internal arbitrary function generator (AFG) and other options. If the price of the instrument is acceptable, the rational choice would be to go for the best device immediately. But in the real world most […]
Understanding the basics: What is characteristic impedance?
We speak of 50- or 75-Ω coaxial cable. The novice wonders if these numbers apply to a given length, say 100 ft. Could you connect an ohmmeter to one end of the cable and expect to get that reading with or without the conductors shunted at the far end? The answer is absolutely not. The characteristic impedance […]