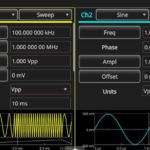
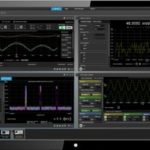
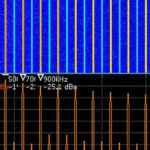
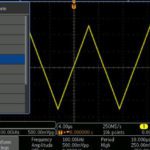
Tektronix today released new firmware for the 5 Series and 6 Series MSO mixed signal oscilloscopes that unlocks a new analysis tool called Spectrum View. A free upgrade, Spectrum View allows you to perform mixed domain analysis on the big, high-resolution displays of the 5 and 6 Series MSOs. This mixed domain capability can be […]
oscilloscope measurements
User review: Connecting the Tektronix AFG 31000 AWG to the MDO3000 oscilloscope
The new Tektronix AFG 31000 Arbitrary Function Generator is noteworthy in that the Home screen, accessed by pressing the Home button on the front panel, permits the user to choose a Basic or Advanced mode. The Basic mode resembles a traditional AFG, with a library of internal waveforms and menus that permit the user to […]
Software tracks, monitors lab instruments, optimizes student learning
The BenchVue Lab Management and Control software tool is designed to simplify the configuration, monitoring and tracking of lab instruments, while optimizing student learning. Keysight’s new BenchVue Lab software application enables educators to spend less time on the manual set-up and tracking of lab instruments and focus on what really matters—providing a high-quality teaching experience. […]
LG U+ adopts Anritsu MT1000A for 5G rollout
Korean operator LG U Plus (LG U+) will use Anritsu’s Network Master Pro MT1000A supporting speeds up to 100 Gbps for 5G service. LG U+ is promoting the expansion of mobile backhaul and fronthaul networks for 5G services using the MT1000A. LG U+ was one Korean mobile network operator to offer LTE, as well as […]
High-def scopes handle three-phase power analysis
A three-phase power analysis software package brings single-phase and three-phase static and dynamic power analysis to the HDO8000A, HDO6000A and WavePro HD 12-bit High Definition oscilloscopes from Teledyne LeCroy. With the 3-Phase Power Analysis software package, research and development engineers can now use Teledyne LeCroy’s 12-bit-resolution oscilloscopes to better understand complex power conversion system and […]
Mitigating ac motor-shaft voltage and bearing currents
Bearing problems are the greatest single contributing factor in motor failure. Often motor damage happens before bearing wear is noticeable. To avoid expensive repairs and costly downtime, early detection is essential. Proper installation of replacement bearings and correct lubrication are critical. It is well known that insufficient lubrication brings early bearing failure, but many maintenance […]
The difference between histograms and spectrograms
Despite their similar names, histograms and spectrograms are totally different ways of displaying a signal or function in a digital storage oscilloscope (DSO). Both are useful in organizing and analyzing electrical waveforms, but the type of information that is displayed and the conclusions that may be drawn from them are worlds apart. Histograms and spectrograms […]
The difference between waveform settings and output settings in Tektronix MDO3000 series oscilloscope internal AFGs
Most digital storage oscilloscopes include an internal arbitrary function generator (AFG). In the Tektronix MDO3000 instrument, there is a port on the back panel labeled AFG Out. To control the AFG and display its output, connect a BNC cable to this port and plug the other end into one of the analog channel inputs or […]
Exploring the difference between a digital oscilloscope and a spectrum analyzer
Traditionally, only the spectrum analyzer was capable of displaying electrical and electromagnetic signals in the frequency domain and the oscilloscope took control of the time domain. More recently, each instrument has become competent in the other’s territory. But this overlapping tendency is far from absolute. Oscilloscopes, working in the Math>FFT mode, have always had a […]
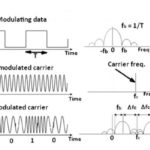
Analog and digital modulation and modulation measurements
In amplitude modulation (AM), the amplitude of a carrier wave whose frequency remains constant changes in response to the modulating signal. In frequency modulation (FM), it is the frequency of the carrier that varies with the amplitude of the modulating signal. The carrier frequency deviates more when the modulating signal amplitude is higher. There are […]